开卷语
俗话说,“熟读唐诗三百首,不会作诗也会吟”。最近收集了很多Android的示例代码,从这些代码的阅读和实验中学习到很多知识,从而产生写这个系列的打算,目标就是一步步跟着实例进行动手实作,真正从“做”中体会和学习Android开发。
本文是这个系列的第一篇,目标是Android自带的一个范例程序:记事本,将分为四篇文章进行详细介绍。
预备知识
搭建开发环境,尝试编写”Hello World”,了解Android的基本概念,熟悉Android的API(官方文档中都有,不赘述)。
程序截图
先来简单了解下程序运行的效果

程序入口点
类似于win32程序里的WinMain函数,Android自然也有它的程序入口点。它通过在AndroidManifest.xml文件中配置来指明,可以看到名为NotesList的activity节点下有这样一个intent-filter,其action为android.intent.action.MAIN,
Category指定为 android.intent.category.LAUNCHER,这就指明了这个activity是作为入口activity,系统查找到它后,就会创建这个activity实例来运行,若未发现就不启动(你可以把MAIN改名字试试)。
<!--<br /><br />Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)<br />http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/<br /><br />--><intent-filter>
<actionandroid:name="android.intent.action.MAIN"/>
<categoryandroid:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER"/>
</intent-filter>
NotesList详解
就从入口点所在的activity(见图1)开始,可以看到这个activity最重要的功能就是显示日志列表。这个程序的日志都存放在Sqlite数据库中,因此需要读取出所有的日志记录并显示。
先来看两个重要的私有数据,第一个PROJECTION字段指明了“日志列表“所关注的数据库中的字段(即只需要ID和Title就可以了)。
<!--<br /><br />Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)<br />http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/<br /><br />-->privatestaticfinalString[]PROJECTION=newString[]{
Notes._ID,//0
Notes.TITLE,//1
};
第二个字段COLUMN_INDEX_TITLE指明title字段在数据表中的索引。
<!--<br /><br />Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)<br />http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/<br /><br />-->privatestaticfinalintCOLUMN_INDEX_TITLE=1;
然后就进入第一个调用的函数onCreate。
<!--<br /><br />Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)<br />http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/<br /><br />-->Intentintent=getIntent();
if(intent.getData()==null)
{
intent.setData(Notes.CONTENT_URI);
}
因为NotesList这个activity是系统调用的,此时的intent是不带数据和操作类型的,系统只是在其中指明了目标组件是Notelist,所以这里把”content:// com.google.provider.NotePad/notes”保存到intent里面,这个URI地址指明了数据库中的数据表名(参见以后的NotePadProvider类),也就是保存日志的数据表notes。
<!--<br /><br />Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)<br />http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/<br /><br />-->Cursorcursor=managedQuery(getIntent().getData(),PROJECTION,null,null,Notes.DEFAULT_SORT_ORDER);
然后调用managedQuery函数查询出所有的日志信息,这里第一个参数就是上面设置的” content:// com.google.provider.NotePad/notes”这个URI,即notes数据表。PROJECTION 字段指明了结果中所需要的字段,Notes.DEFAULT_SORT_ORDER 指明了结果的排序规则。实际上managedQuery并没有直接去查询数据库,而是通过Content Provider来完成实际的数据库操作,这样就实现了逻辑层和数据库层的分离。
<!--<br /><br />Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)<br />http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/<br /><br />-->SimpleCursorAdapteradapter=newSimpleCursorAdapter(this,R.layout.noteslist_item,cursor,
newString[]{Notes.TITLE},newint[]{android.R.id.text1});
setListAdapter(adapter);
查询出日志列表后,构造一个CursorAdapter,并将其作为List View的数据源,从而在界面上显示出日志列表。可以看到,第二个参数是R.layout.noteslist_item,打开对应的noteslist_item.xml文件,
<!--<br /><br />Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)<br />http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/<br /><br />--><TextViewxmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@android:id/text1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="?android:attr/listPreferredItemHeight"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:paddingLeft="5dip"
android:singleLine="true"
/>
就是用来显示一条日志记录的TextView,最后两个字段指明了实际的字段映射关系,通过这个TextView来显示一条日志记录的title字段。
处理“选择日志”事件
既然有了“日志列表”,就自然要考虑如何处理某一条日志的单击事件,这通过重载onListItemClick方法来完成,
<!--<br /><br />Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)<br />http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/<br /><br />-->@Override
protectedvoidonListItemClick(ListViewl,Viewv,intposition,longid){
Uriuri=ContentUris.withAppendedId(getIntent().getData(),id);
Stringaction=getIntent().getAction();
if(Intent.ACTION_PICK.equals(action)||Intent.ACTION_GET_CONTENT.equals(action)){
//Thecalleriswaitingforustoreturnanoteselectedby
//theuser.Thehaveclickedonone,soreturnitnow.
setResult(RESULT_OK,newIntent().setData(uri));
}else{
//Launchactivitytoview/editthecurrentlyselecteditem
startActivity(newIntent(Intent.ACTION_EDIT,uri));
}
}
首先通过”content:// com.google.provider.NotePad/notes”和日志的id 号拼接得到选中日志的真正URI,然后创建一个新的Intent,其操作类型为Intent.ACTION_EDIT,数据域指出待编辑的日志URI(这里只分析else块)。
Intent深度剖析
那么,上面这句startActivity(new Intent(Intent.ACTION_EDIT, uri))执行后会发生什么事情呢?这时候Android系统就跳出来接管了,它会根据intent中的信息找到对应的activity,在这里找到的是NoteEditor这个activity,然后创建这个activity的实例并运行。
那么,Android又是如何找到NoteEditor这个对应的activity的呢?这就是intent发挥作用的时刻了。
<!--<br /><br />Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)<br />http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/<br /><br />-->newIntent(Intent.ACTION_EDIT,uri)
这里的Intent.ACTION_EDIT=” android.intent.action.EDIT”,另外通过设置断点,我们看下这里的uri值:
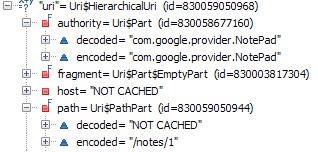
可以看到选中的日志条目的URI是:content://com.google.provider.NotePad/notes/1
然后我们再来看下Androidmanfest.xml,其中有这个provider
<!--<br /><br />Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)<br />http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/<br /><br />--><providerandroid:name="NotePadProvider"
android:authorities="com.google.provider.NotePad"
/>
发现没有?它也有com.google.provider.NotePad,这个是content://com.google.provider.NotePad/notes/1的一部分,同时
<!--<br /><br />Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)<br />http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/<br /><br />--><activityandroid:name="NoteEditor"
android:theme="@android:style/Theme.Light"
android:label="@string/title_note"
android:screenOrientation="sensor"
android:configChanges="keyboardHidden|orientation"
>
<!--Thisfiltersaysthatwecanvieworeditthedataof
asinglenote-->
<intent-filterandroid:label="@string/resolve_edit">
<actionandroid:name="android.intent.action.VIEW"/>
<actionandroid:name="android.intent.action.EDIT"/>
<actionandroid:name="com.android.notepad.action.EDIT_NOTE"/>
<categoryandroid:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/>
<dataandroid:mimeType="vnd.android.cursor.item/vnd.google.note"/>
</intent-filter>
<!--Thisfiltersaysthatwecancreateanewnoteinside
ofadirectoryofnotes.-->
<intent-filter>
<actionandroid:name="android.intent.action.INSERT"/>
<categoryandroid:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/>
<dataandroid:mimeType="vnd.android.cursor.dir/vnd.google.note"/>
</intent-filter>
</activity>
上面第一个intent-filter中有一个action 名为android.intent.action.EDIT,而前面我们创建的Intent也正好是
Intent.ACTION_EDIT=” android.intent.action.EDIT”,想必大家已经明白是怎么回事了吧。
下面就进入activity选择机制了:
系统从intent中获取道uri,得到了content://com.google.provider.NotePad/notes/1,去掉开始的content:标识,得到com.google.provider.NotePad/notes/1,然后获取前面的com.google.provider.NotePad,然后就到Androidmanfest.xml中找到authorities为com.google.provider.NotePad的provider,这个就是后面要讲的contentprovider,然后就加载这个content provider。
<!--<br /><br />Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)<br />http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/<br /><br />--><providerandroid:name="NotePadProvider"
android:authorities="com.google.provider.NotePad"
/>
在这里是NotePadProvider,然后调用NotePadProvider的gettype函数,并把上述URI传给这个函数,函数返回URI所对应的类型(这里返回Notes.CONTENT_ITEM_TYPE,代表一条日志记录,而CONTENT_ITEM_TYPE = " vnd.android.cursor.item/vnd.google.note ")。
<!--<br /><br />Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)<br />http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/<br /><br />-->@Override
publicStringgetType(Uriuri){
switch(sUriMatcher.match(uri)){
caseNOTES:
returnNotes.CONTENT_TYPE;
caseNOTE_ID:
returnNotes.CONTENT_ITEM_TYPE;
default:
thrownewIllegalArgumentException("UnknownURI"+uri);
}
}
上面的sUriMatcher.match是用来检测uri是否能够被处理,而sUriMatcher.match(uri)返回值其实是由
<!--<br /><br />Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)<br />http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/<br /><br />-->sUriMatcher=newUriMatcher(UriMatcher.NO_MATCH);
sUriMatcher.addURI(NotePad.AUTHORITY,"notes",NOTES);
sUriMatcher.addURI(NotePad.AUTHORITY,"notes/#",NOTE_ID);
决定的。
然后系统使用获得的" vnd.android.cursor.item/vnd.google.note "和”android.intent.action.EDIT”到androidmanfest.xml中去找匹配的activity.
<!--<br /><br />Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)<br />http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/<br /><br />--><intent-filterandroid:label="@string/resolve_edit">
<actionandroid:name="android.intent.action.VIEW"/>
<actionandroid:name="android.intent.action.EDIT"/>
<actionandroid:name="com.android.notepad.action.EDIT_NOTE"/>
<categoryandroid:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/>
<dataandroid:mimeType="vnd.android.cursor.item/vnd.google.note"/>
</intent-filter>
正好NoteEditor这个activity的intent-filter满足上述条件,这样就找到了NoteEditor。于是系统加载这个类并实例化,运行,然后就到了NoteEditor的OnCreate函数中(见后续文章)。
小技巧
1,在命令行中使用”adb shell”命令进入系统中,然后”cd app”进入应用程序所在目录,”rm XXX”就可以删除你指定的apk,从而去掉其在系统顶层界面占据的图标,若两次”cd data”则可以进入应用程序使用的数据目录,你的数据可以保存在这里,例如Notepad就是把其数据库放在它的databases目录下,名为note_pad.db.
2,第一次启动模拟器会比较慢,但以后就别关闭模拟器了,修改代码,调试都不需要再次启动的,直接修改后run或debug就是。
作者:phinecos(洞庭散人)
出处:http://phinecos.cnblogs.com/
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但请保留此段声明,并在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接
分享到:
















相关推荐
Android实例剖析笔记 Android实例剖析笔记
Android实例教程 会员贡献索引贴 实用Android开发工具和资源精选 APK权限大全 - Android必懂知识 最无私的Android资料(书籍+代码)分享[总结] Android中文帮助教程(非常合适新手入门) android程序编写及调试...
主要介绍了Android学习笔记之应用单元测试,结合实例形式较为详细的分析了Android单元测试的实现原理与具体步骤,具有一定参考借鉴价值,需要的朋友可以参考下
1. 入门实例剖析1 2 2.在测试时,如何实现一个提示 8 3.可以使用AlertDialog.Builder 才产生一个提示框. 9 4. menu 的用法. 10 1. 简单的代码 10 2. menu实现的两种方法 10 5.Activity 的切换(含Bundle传值) 14 1. ...
主要介绍了Android学习笔记之ActionBar Item用法,结合实例形式分析了ActionBar Item的具体功能与相关使用技巧,需要的朋友可以参考下
主要介绍了Android开发之电话拨号器,结合实例形式详细分析了Android电话拨号器的实现步骤与具体代码,并附带了一个Android开放电话拨号器的学习笔记,需要的朋友可以参考下
本文实例讲述了Android编程中全局变量。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下: 现在每天都在忙,而且一忙起来,就把写笔记的事情放在了后面,最近在写程序的时候,突然要使用全局变量,就按照以前的方式,写了一个类,...
中的实例,来分析 ViewGroup 的事件分发机制。 本章介绍 View(视图) 动画相关概念以及应用。 本篇介绍 Handler 和 Message 以及 Looper 的基本用法和工作原理。 本篇介绍 AsyncTask 的使用方法和工作原理 本篇介绍 ...